Contents
Key Takeaways
- Anti-fog and anti-scratch coatings are real, bonded technologies tested for durability.
- Anti-fog coatings control moisture, while anti-scratch coatings add a hard protective layer.
- Coatings are tested to meet ANSI Z87.1+ standards, with optional K and N markings.
- Proper cleaning, handling, and storage are essential to maintain coating effectiveness.
- Permanent coatings often last the lifetime of the lens, while temporary solutions wear off quickly.
Foggy or scratched safety glasses aren’t just annoying, they can create real safety hazards. Fog blocks vision in humid or rapidly changing environments, while scratches distort sight, increasing the risk of accidents. In U.S. workplaces, eye injuries cost hundreds of millions annually in medical and indirect costs.
But are anti-scratch and anti-fog coatings a real solution or just a marketing scheme?
How Does Fogging Occur in the Workplace?
Fogging happens when warm, humid air comes into contact with a cooler lens surface, causing moisture in the air to condense into tiny droplets. These droplets scatter light and reduce visibility, creating a safety hazard.
Common environments where fogging is an issue:
- Cold storage or refrigerated areas: Lenses fog when workers move from warm areas to cold rooms.
- Welding and hot work: Sudden temperature changes and perspiration increase condensation risk.
- HVAC, plumbing, or mechanical work: Tight spaces with high humidity can cause rapid lens fogging.
Removing safety eyewear to clear fog is dangerous because it exposes the eyes to flying debris, sparks, chemicals, or sharp tools, increasing the likelihood of accidents. Clear, anti-fog lenses ensure continuous eye protection in these high-risk environments.
Is The Anti-Fog Coating Fact or Fiction?
Anti-fog and anti-scratch coatings are real, scientifically developed technologies. Anti-fog coatings were first developed by NASA in the 1960s to prevent condensation inside astronaut helmets. Anti-scratch coatings, typically made from diamond-like carbon or ceramic layers, protect softer polycarbonate lenses without reducing impact resistance.
These coatings address a key challenge: anti-fog is hydrophilic to manage moisture, while anti-scratch is hard and non-porous to resist abrasion. High-quality lenses combine the two, usually with anti-scratch on the outside and anti-fog on the inside, keeping vision clear and lenses durable under extreme conditions.
Modern lens coatings are tested, certified, and essential for any work environment where eye protection cannot be removed.
How Does Anti-Fog Coating Work?
Fog forms when moisture in the air condenses on a lens surface. This happens whenever the lens is colder than the surrounding air, creating thousands of tiny water droplets that scatter light and block vision. In workplaces, fogging can force workers to remove eye protection, creating a serious safety risk.
Anti-fog coatings manage moisture to prevent condensation. There are two main types:
1. Hydrophilic Coatings (water-loving):
- Attract and spread moisture into a thin, transparent layer instead of droplets.
- Reduce surface tension, preventing scattered droplets that obscure vision.
- Common in permanent, high-performance workplace eyewear.
2. Hydrophobic Coatings (water-repelling):
- Cause water to bead up and roll off the lens surface.
- More effective in moderate humidity, less common in high-risk industrial settings.
In professional safety glasses, anti-fog coatings are usually applied to the inside of the lens, where heat, sweat, and breath from the wearer create the highest risk of fogging. By controlling how water interacts with the lens, these coatings ensure workers maintain clear, uninterrupted vision.
How Does Anti-Scratch Coating Work?
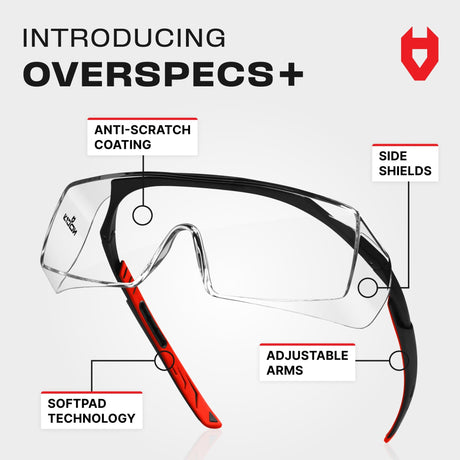
Polycarbonate lenses are highly impact-resistant, making them ideal for ANSI-rated safety eyewear, but they are naturally soft and prone to scratches. Scratched lenses reduce clarity, force frequent replacements, and can compromise worker safety.
Anti-scratch coatings are transparent, extremely hard layers, often made from diamond-like carbon (DLC) or ceramic compounds, permanently bonded to the lens surface. These coatings increase surface hardness, protecting lenses from everyday wear, cleaning, and debris, while leaving impact resistance unaffected.
High-quality safety eyewear typically applies the anti-scratch coating to the outside of the lens, as the surface is exposed to dust, debris, and frequent wiping. Paired with an inner anti-fog layer, this combination ensures lenses remain clear, durable, and reliable under demanding workplace conditions.
Hard coatings rely on advanced material engineering. DLC or ceramic layers provide excellent resistance to abrasion. They are applied through chemical or physical bonding, forming a thin, transparent barrier that preserves both clarity and impact protection.
Can Safety Glasses Have Both Anti Fog And Scratch Tech?
Safety glasses can have both anti-fog and anti-scratch tech. However, the two coatings have fundamentally different chemical properties. Anti-fog coatings are hydrophilic, designed to manage moisture and prevent condensation. Anti-scratch coatings are hard and non-porous, built to resist abrasion and protect the lens surface.
Because these properties are essentially opposite, combining them on a single lens requires separate, targeted application. In high-quality safety eyewear:
- The outside of the lens receives the anti-scratch coating, guarding against dust, debris, and cleaning wear.
- The inside of the lens receives the anti-fog coating, where condensation from breath, sweat, and heat is most likely.
This dual-layer design allows lenses to remain clear, durable, and reliable, even in extreme workplace conditions, without compromising impact resistance or optical clarity.
How Are Anti-Fog and Anti-Scratch Coatings Tested?
Both anti-fog and anti-scratch coatings undergo rigorous testing to ensure performance under real-world conditions. These tests focus on clarity, durability, and effectiveness, rather than general impact resistance (which is covered by ANSI Z87.1 separately).
Anti-Fog Testing:
- Coatings are evaluated in humidity and temperature chambers to simulate fog-prone environments.
- Performance is measured by how long the lens remains clear without wiping and how uniformly moisture spreads across the surface.
- ANSI Z87.1 marking X (or N for the European EN166 standard) is given to lenses that meet the standard for anti-fog performance, verifying consistent fog prevention.
Anti-Scratch Testing:
- Coatings are subjected to abrasion and wear tests, such as the Bayer Abrasion Test, which simulates repeated contact with dust, cleaning cloths, and debris.
- Lenses are scored on their resistance to visible scratches, demonstrating durability over time.
- EN166 optional marking K identifies lenses with verified superior scratch resistance.
These tests confirm that the coatings maintain clarity and durability, ensuring workers can rely on their eyewear in demanding environments. By separating anti-fog and anti-scratch layers, manufacturers can optimize each coating without compromising the other, guaranteeing long-lasting performance.
Are Permanent Coatings As Good As Temporary Solutions?
Anti-fog and anti-scratch coatings are available in permanent and temporary forms, and understanding the difference is critical for workplace safety.
Permanent Coatings:
- Bonded during manufacturing using methods like heat-curing or flow coating.
- Designed to last the lifetime of the lens under normal use.
- High-performance coatings, such as those in professional safety eyewear, maintain consistent anti-fog and scratch resistance in demanding environments.
- They are ideal for workplaces where reliable, maintenance-free protection is essential.
Temporary Coatings:
- Include sprays, wipes, or gels applied by the user.
- Provide short-term protection, but effectiveness diminishes with cleaning, abrasion, or exposure to harsh conditions.
- Often unsuitable for high-risk or industrial settings, as lenses may lose clarity or protection quickly.
For workplaces where eye protection is mandatory and cannot be removed, permanent, factory-applied coatings are the only reliable option to ensure long-term clarity and durability, reducing downtime and replacement costs.
How To Take Care Of Safety Glasses To Protect The Coatings?
Even the best anti-fog and anti-scratch coatings require proper handling to maintain performance:
- Cleaning: Use a microfiber cloth and lens-safe cleaner. Avoid paper towels, tissues, or abrasive materials that can damage coatings.
- Avoid Touching: Finger oils can degrade anti-fog surfaces over time.
- Storage: Keep eyewear in a protective case when not in use to prevent scratches and dust buildup.
- Environment: Avoid prolonged exposure to harsh chemicals or extreme temperatures, which can reduce coating effectiveness.
Following these guidelines helps maintain clarity, durability, and the full lifespan of both anti-fog and anti-scratch coatings.
Conclusion
Foggy or scratched lenses are more than minor inconveniences; they are serious workplace hazards. Modern anti-fog and anti-scratch coatings, developed from NASA research and advanced material science, provide clear vision, durability, and reliable protection.
By using high-quality, ANSI-certified safety eyewear with these coatings, workers can maintain visibility in humid, hot, or dusty environments without removing their protection. Choosing permanently coated lenses ensures long-term performance, reducing accidents, downtime, and replacement costs.
In short, investing in professional anti-fog and anti-scratch coatings is critical for worker safety, productivity, and compliance.
FAQ
How long do permanent anti-fog coatings last?
Designed for the lens’s lifetime with proper care, though harsh conditions or improper cleaning can reduce effectiveness.
Do DIY anti-fog tricks like saliva or soap work?
They might; however, they offer temporary results and may damage polycarbonate lenses. Professional coatings are more reliable.
Can I apply temporary anti-scratch coatings over permanent ones?
It’s not recommended as temporary coatings may interfere with the permanent layer and reduce durability.
Do coatings affect impact resistance?
No. Coatings are tested to meet ANSI Z87.1+ standards and do not compromise lens safety.
How should I clean coated safety glasses?
Use a microfiber cloth and lens-safe cleaner. Avoid paper towels, tissues, or abrasive materials.
How can I tell if my lenses are properly coated?
Look for the K (scratch) and N (fog) symbols on the lens or frame, along with ANSI Z87+ markings.